A new dawn for forests: technologies for reforestation and conservation
Discover how technological advancements are revolutionizing reforestation and conservation efforts, making them more efficient and effective. From satellite imaging and genetic engineering to artificial intelligence and blockchain, technology offers new ways to monitor, predict, and intervene in environmental challenges.
To stop climate change, preserve biodiversity, and help local populations, reforestation, and conservation are crucial. Even though there is an obvious need for these projects, using conventional means is frequently expensive, labor-intensive, and time-consuming.
As the 21st century progresses, technological breakthroughs are starting to provide potential answers to these problems. Today, we’ll examine how technological advancements are transforming conservation and reforestation initiatives, making them more effective and efficient than ever. However, a review is necessary first:
What is reforestation?
Reforestation is the process of restoring forests that have been destroyed by logging, mining, or other human activity or by the effects of natural catastrophes. To regenerate and restore these regions back to their natural state, it entails sowing tree seedlings or seeds in places where forests have been reduced to bare ground.
Due to trees’ ability to absorb carbon dioxide, store carbon, and create oxygen, reforestation is essential for lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, it promotes biodiversity by creating homes for different species and by sustaining human lives via the provision of resources and ecological services.
What is conservation?
Conservation, on the other hand, involves the protection, preservation, management, or restoration of natural environments and the biodiversity within them. This includes ecosystems such as forests, wetlands, grasslands, and marine areas. The aim of conservation is to protect species from extinction, maintain biodiversity, and ensure the sustainable use of natural resources.
Conservation efforts can be proactive, focusing on the prevention of degradation or destruction of habitats, or reactive, aiming to restore or rehabilitate damaged ecosystems. But the bottom line is that both conservation and reforestation are crucial to maintain the balance of our planet and to mitigate the effects of climate change.
Technology’s role in addressing climate change
Technology offers several key advantages over traditional methods in addressing climate change.
First, it enhances efficiency. Technological solutions often automate and speed up processes, allowing for greater scale and speed than manual methods.
Second, technology provides more precise and accurate data. Modern sensors and monitoring systems can gather comprehensive, real-time data about the environment, allowing for more informed decisions and interventions. This precision is often beyond the reach of traditional observation methods.
Third, technology enables better predictive capabilities. Advanced computing and artificial intelligence can process large amounts of data to forecast future trends and scenarios, which aids in proactive planning and mitigation — something that’s not possible with traditional methods.
Fourth, technology allows for greater accessibility and reach. Some tools, like satellites and drones, can access areas that are difficult to reach by humans, ensuring all areas are covered in conservation and reforestation efforts.
Finally, technology can offer more sustainable and less intrusive solutions. Unlike some traditional methods that can be harmful to the environment, many modern technologies prioritize sustainability and minimal environmental impact.
In the context of reforestation and conservation, technology can range from drones and satellite imagery to genetic engineering and artificial intelligence. These tools can assist in various processes, including seed sowing, forest monitoring, predictive modeling, wildlife tracking, and more.
Satellite imaging and GIS
Satellite imaging, coupled with Geographic Information System (GIS), provides valuable data on forest growth and health. These technologies make it possible to monitor large areas of land, detect changes in vegetation, and even predict potential problems like disease or drought. This proactive approach allows conservationists to intervene promptly, ensuring the maximum survival rate for newly planted forests.
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering is another avenue being explored for reforestation. By modifying the genetic makeup of trees, scientists can potentially enhance their growth and survival rates, enabling forests to recover quicker from deforestation. However, the ethical considerations associated with genetic modification must be carefully considered to ensure responsible use.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in conservation
AI is proving to be a formidable tool in environmental conservation. Machine learning algorithms can predict environmental changes, track wildlife patterns, and even identify illegal logging. According to The UN Specialised Agency for ICTs, by providing real-time data and predictive capabilities, AI can help to mitigate the impacts of environmental damage, offering a new level of efficiency to conservation efforts.
Internet of Things (IoT) and smart devices
IoT and smart devices are also used to monitor and manage forest ecosystems. Sensors can track temperature changes, water levels, and wildlife activity, feeding this information back to central systems for analysis. This technology provides conservationists with the information they need to maintain healthy ecosystems and protect endangered species.
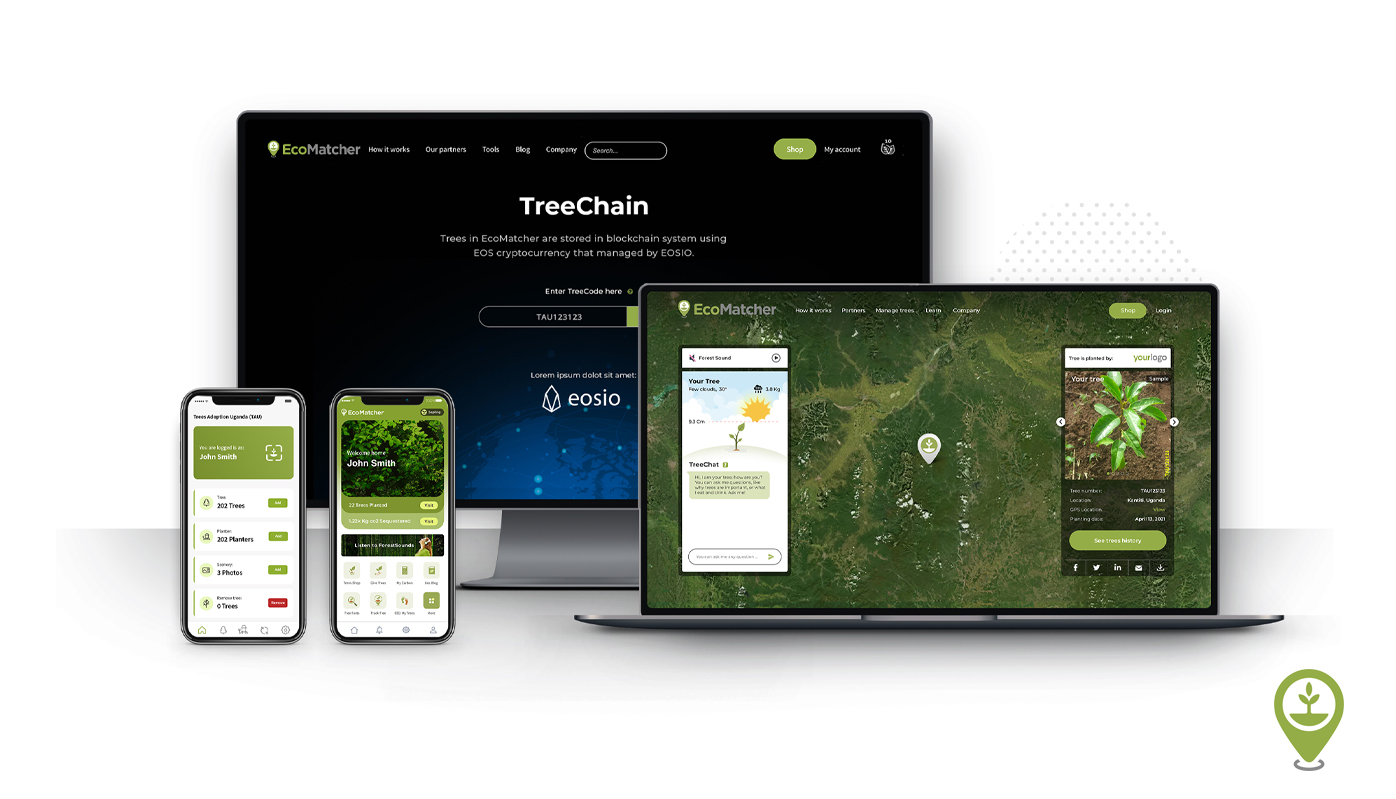
Blockchain for conservation and reforestation
Blockchain technology, best known for its role in cryptocurrency, is being used to foster transparency and trust in conservation and reforestation efforts. Blockchain can be used to track donations, verify the legitimacy of projects, and ensure that funds are used efficiently and effectively. It’s a powerful tool for building donor confidence and driving forward successful conservation initiatives.
EcoMatcher swears by blockchain to provide transparency in tree planting. Every tree that has been planted or will be planted by EcoMatcher is stored and visible on the TreeChain. It is based on the EOSIO protocol, the leading open-source blockchain platform that enables transparency in transactions. TreeChain is carbon neutral as EcoMatcher offsets its carbon footprint with trees.
Drones for reforestation
Drones are transforming the way we approach large-scale tree planting. They can sow thousands of seeds per day, covering vast areas far more rapidly than any human crew could. Not only do they cut down on physical labor, but they also allow access to steep or otherwise inaccessible areas. The benefits are twofold: increasing the pace of reforestation and reaching locations that were previously left out.
Future prospects and challenges
The future of reforestation and conservation looks promising with these technological advancements. However, the adoption of these technologies is not without barriers. Ethical considerations, particularly in areas like genetic engineering and AI, must be addressed. Furthermore, the cost of these technologies can be prohibitive, and their use requires specific expertise.
Despite these challenges, there’s a growing need for increased investment and research in these technologies. With more backing, these tools can become widely accessible and more effective, paving the way for a greener future.
The final word
Technology is providing us with powerful tools to combat deforestation and conserve our ecosystems. While there are still hurdles to overcome, the potential benefits far outweigh these challenges. By embracing these advancements, we can work towards efficient, effective reforestation and conservation initiatives that can not only preserve our planet but also ensure its flourishing future.

